Grand Prix motorcycle racing is one of the most exciting and technical sports in the world. But, some of the key phrases in this sport can be wheelie confusing. Here is a glossary of terms to get you up to speed before the Australian Motorcycle Grand Prix on October 17.
Average speed:A statistic measured by the distance covered in a lap or race, divided by the time it took to complete. Average speed is usually compared with total race and lap times which are good measures of performance.
Blistering:An uncommon characteristic of modern MotoGP tyres which is seen when they burn at high temperatures. Blisters are usually visible to the exterior of the tyre and appear as small cuts on the rubber. Historically, there have been many issues regarding blistering at the Australian MotoGP Grand Prix, so keep an eye out for it.
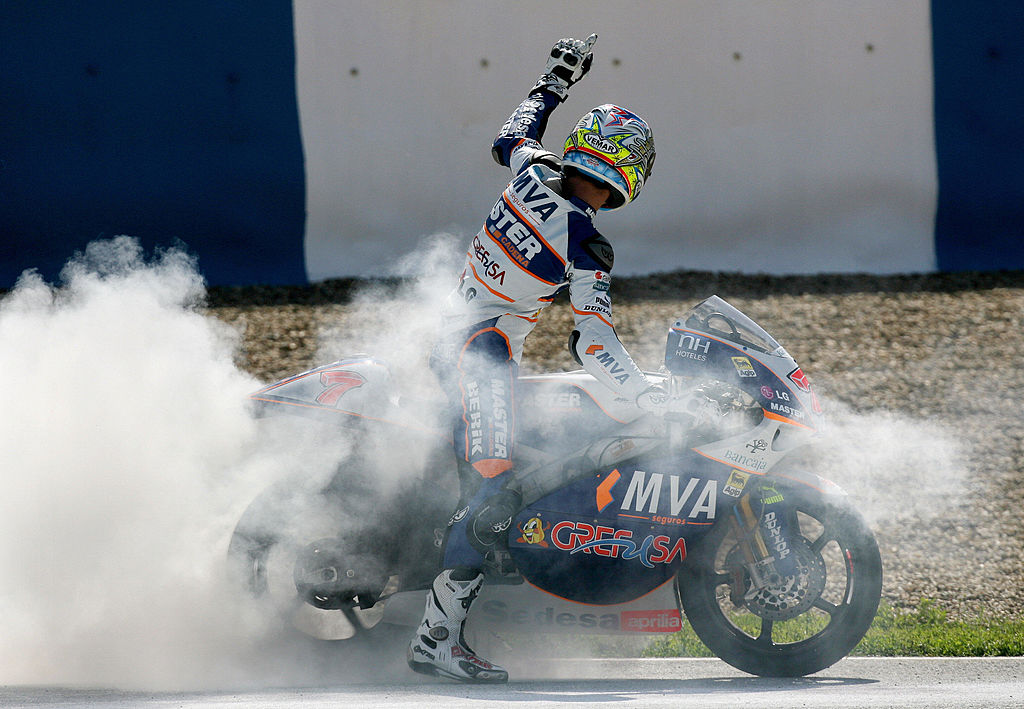
Burnout:The action of keeping the front wheel stationary and skidding the back wheel to create a friction which heats the tire and produces smoke. They are most commonly used by riders in celebration but are highly discouraged by race officials as they are dangerous and wreak damage on the engine.

CC (cubic centimetre):Unit of measurement regarding volume in the chamber of the bike’s engine. As the CC increases, the amount of air flowing through the engine becomes larger. This allows for more power to be produced. All MotoGP bikes have 1000cc engines.
Did not finish (DNF):Rider didn’t complete the race.
Did not attend (DNA):Rider wasn’t present for race.
Did not qualify (DNQ):Rider didn’t make it through the qualification stage.
Disqualified (DSQ):Rider has been forced to abandon the race and is unable to retrieve any obtained points.

Did not start (DNS):Rider didn’t start the race.
Drag:Term referring to the force (either air or water) opposing the motion of the rider. There are measures taken to limit the amount of drag experienced by a rider in a race, including body posture and helmet design.
Electrical Control Unit (ECU):System which controls most functions within the bike. Racing teams can change the settings on the ECU to fit the rider’s needs, such as traction and engine control.
Formation Lap:Riders complete this lap moments before the race commences. The formation lap warms up the tyres and the brakes, allowing for peak performance during the race. It also gives the racing team an opportunity to ensure all systems are functioning correctly.
MotoGP:The most recognised, well-renowned competition of motorcycle racing in the world. In this league, there are 20 Grand Prix races in one season and by the end, there is one champion.
Kerb:The edges of the track which are typically painted with two striped colours. They help guide riders around bends and keep them on track. Although, riding on this section of the track will slow racers down and can cause bike damage.

Lean Angle:The angle between the vertical and the rider’s body axis when leaning around a bend.

Pitlane:A byway where teams’ garages are situated which lies adjacent to the racetrack. Riders will enter these areas during practice and qualification sessions to refuel, adjust settings, check for any issues, ETC. There is a strict 60km/h speed limit in this area. It is rare to see a rider enter the pitlane during a Grand Prix race as it will slow them down significantly.
Pit Crew:Group of people in the rider’s pitlane who help with any issues regarding the bike. There can only be five pit crew members and they usually consist of mechanics and engineers.

Pole Position:The first place on the grid, given to the rider who finishes first in the qualification process. It offers the rider who completes the qualification stage fastest, the opportunity to have the best possible start.
Points:Reward given to riders following their place in a Grand Prix Race. Those who finish in the first 15 places receive points. At the end of the season, the points from each Grand Prix are accumulated and whoever has the most is crowned MotoGP Champion.
Pull:The moment where a rider suddenly attempts to hit top-speed and separate themselves from surrounding bikes. Riders use this strategically, as it will wear-out their tyres if they ‘pull’ too often.

Qualifying Stage:The process which determines the rider’s starting place. Racers attempt to get the fastest time possible on the track and then, they are ranked. The fastest time in the qualifying stage is placed into pole position.
Ride Through:A sanction for the rider which involves entering and exiting through the pitlane, forcing a slowed time. This is usually a result of a false start or foul play.
Slipstream:When a rider tailgates another down a straight, to reduce the amount of drag they experience. This allows racers to reach higher speeds quicker and it’s also useful in overtaking.
Yellow Flag:A yellow flag indicates that a danger is present in a particular area of the circuit. It also prohibits riders from overtaking in this area.
Catch all the action from the Australian Motorcycle Grand Prix live and free on 10 and 10 play on October 17.